- Home
- Medications
- List of Migraine Medications
List of Migraine Medications: How To Pick The Best One
When you live with migraine, the right medication can be life changing and the wrong one can be useless (or worse, harmful). Below you’ll find a complete, organized, and doctor ready list of migraine medications, including the newest CGRP drugs, proven triptans, preventive options, and safe over-the-counter choices. This resource is designed to help you understand what’s available, prepare for a productive conversation with your healthcare provider, and choose a treatment plan that’s right for your needs.
Tip: You can also grab my printable migraine medication list to take to your next appointment - it’s instantly downloadable.
Disclaimer: This page provides general educational information and is not medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting, changing, or stopping any migraine treatment.
Just scroll down or click on a link to go straight to the section you need most.
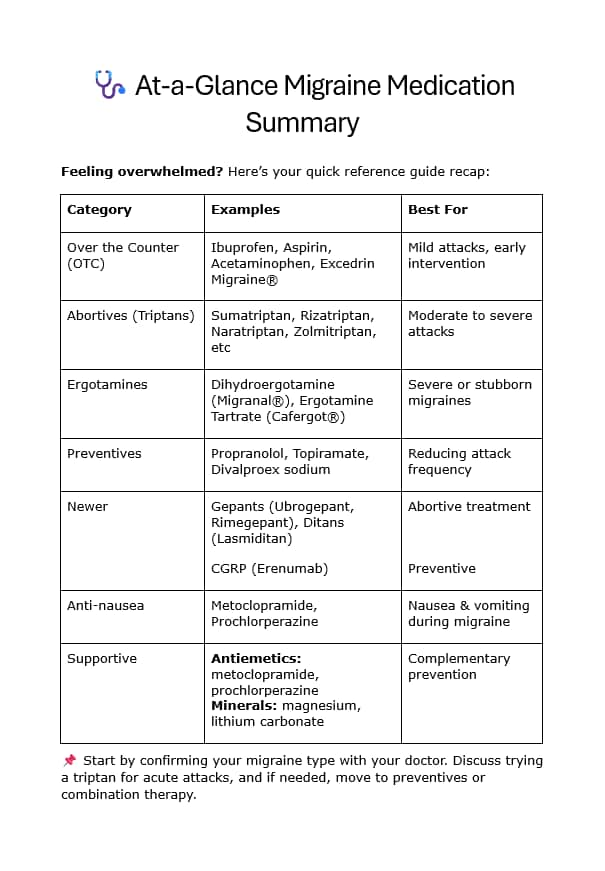
Quick Reference: Migraine Medications by Category
For a quick overview - ideal for your next doctor visit.
Acute (Abortive) Treatments
- OTC: Ibuprofen, aspirin, acetaminophen, Excedrin Migraine®
- Triptans: sumatriptan, rizatriptan, zolmitriptan, naratriptan, etc.
- Ergots: dihydroergotamine, ergotamine tartrate
- Newer: gepants (ubrogepant, rimegepant), ditans (lasmiditan)
- Combination: sumatriptan + naproxen (Treximet™)
Preventive Treatments
- Beta-blockers: propranolol, timolol, metoprolol
- Anticonvulsants: topiramate, valproate
- Antidepressants: amitriptyline, nortriptyline
- CGRP monoclonal antibodies: erenumab, fremanezumab, galcanezumab, eptinezumab
- Botox® for chronic migraine
Supportive / Adjunct
- Antiemetics: metoclopramide, prochlorperazine
- Minerals: magnesium, lithium carbonate
>> Download: Printable List of Migraine Medications - $4.99 to take to your doctor.
Understanding Migraine Medications
Migraine medications fall into two main categories or purposes:
- Acute (abortive): Taken before or during an attack to stop the cycle from progressing, also reduces symptoms.
- Preventive: Taken daily to reduce frequency and severity of attacks.
A third group - supportive medications - help manage associated symptoms like nausea.
>> Download: Printable List of Migraine Medications - $4.99 to take to your doctor.
1. Over the Counter (OTC) Migraine Medications
FDA-approved OTC products for migraine pain:
- Excedrin Migraine® - Acetaminophen + Aspirin + Caffeine
- Advil Migraine® - Ibuprofen
- Motrin Migraine Pain® - Ibuprofen
The ingredients for Excedrin combine acetaminophen, aspirin and caffeine. It is recommended for reducing migraine pain and the accompanying symptoms.
Both Advil and Motrin contain ibuprofen. They are recommended to treat headaches and the associated pain.
Pros: Widely available, inexpensive.
Cons: Risk of stomach issues, rebound headaches, and cardiovascular side effects if overused.
Caution: Even OTC drugs have risks. NSAIDs can cause GI, kidney, and cardiovascular issues; acetaminophen can damage the liver in high doses.
Personal notes: None of these alone ever helped reduce my severe migraine pain or abort an attack. Combining ibuprofen with a triptan was my breakthrough.
Headache tablets are not recommended for migraine attacks as they perform the wrong action. I have clients that say they take Mersyndol for the pain and then take too many when they don't work. There is a risk of overdose.
Let's get clear on what works for migraines then you can discuss these with your doctor to find what will work best for you.
A 2015 Cochrane review proved that evidence based acute migraine treatments showed the top 9 treatments researched to abort attacks. If you were to try each one separately at the onset of a migraine attack, the statistics show over a 90% chance that one of the treatments could reduce your pain levels from moderate/severe to NO pain within 2 hours. [3]
For Moderate/Severe to NO pain within 2 hours: Sumatriptan Injection ranks the highest at 59%. This fell by half using oral delivery at the 100mg dose but patients still experienced a reduction to mild pain effectively within 2 hours. Then comes Zolmitriptan 2.5mg oral, Ibuprofen 200 or 400mg oral, Sumatriptan Nasal Spray, Aspirin 1000mg oral, Diclofenac 50mg oral, Paracetamol 100mg oral, and last is Naproxen 500mg or 825mg oral. Naproxen is not a good drug to treat migraines, it was only slightly more effective than the placebo.
The takeaway: Sumatriptan via injection is found to be one of the most effective (and more expensive) migraine treatments, and then Sumatriptan in oral form and Zolmitriptan in oral form. According to this data, the most effective over the counter medication (NSAID) to use is Ibuprofen. For the fastest action try the soluble formulations that dissolve in water.
Side effects: This is what drugs.com says about Motrin Migraine Pain: "This medicine may cause life-threatening heart or circulation problems such as heart attack or stroke, especially if you use it long term."
Always discuss the potential side effects with your doctor before you take anything, or the pharmacist. And work closely with your doctor to find a combination that works for you.
OTC Tips:
- Use soluble forms for faster absorption
- Avoid daily use to prevent rebound headaches
- Always check interactions with other meds
2. Abortive Medications: Triptans (Serotonin 5HT1B/1D Agonists)
Triptans are first-line prescription drugs for the acute treatment of moderate to severe migraine attacks.
A-Z list of migraine medications:
- Almotriptan (Axert®)
- Eletriptan (Relpax®)
- Frovatriptan (Frova®)
- Naratriptan (Amerge®, Naramig®) seems to be working the best for me long term.
- Rizatriptan (Maxalt®) is available as a rapidly dissolving tablet. This one is peppermint flavored and the wafer dissolves on your tongue. It didn't even feel like I took anything. Fantastic for those of us who experience nausea as a symptom. However, it was not long enough acting for my long episodes, so taking four just for one migraine made me nervous. And then waiting to take more in the recommended time ironically resulted in more nausea and vomiting.
- Sumatriptan (Imitrex®, Imigran®) is available in many delivery forms: nasal spray, self-injection, tablets and fast dissolving pills. I found the 50mg tablet really strong. My heart attack like side effects were just too much to bear. But it aborted the migraine and boy did I feel euphoric after that.
Research Insight: Sumatriptan injection is the most effective at 59% of individuals achieving pain-free status within 2 hours.
- Treximet™ - combination of Sumatriptan and Naproxen Sodium. It's a (NSAID) non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. It is used frequently with great success, but there are some strong warnings with this medication, it can greatly increase your risk of stroke or heart attack.
- Zolmitriptan (Zomig®) available in tablets and nasal spray. Too strong for me! I experienced hot flushes and heart attack like side effects.
Delivery forms: tablets, rapidly dissolving wafers, nasal sprays, self-injections.
Common side effects: chest tightness, flushing, dizziness. I recommend asking your pharmacist for the full print out that has the other contra indicated medications and side effects for what you have been prescribed. For example, you can’t take a triptan with another form of triptan, ergotamine, or SSRI’s (selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors).
Not for: people with certain heart or vascular conditions.
Important Safety Notes:
- Never mix different triptans or combine with ergotamines
- Avoid if you have uncontrolled hypertension or heart disease
- Watch for serotonin syndrome with SSRIs
- Have very clear instructions from your doctor about how many triptans you can take during one attack. When you can take another dose if needed. What is a maximum if you have say a 5-7 day long migraine attack. Take your worse case scenario so you can prepare ahead for that.
I've written more about Triptans here >> Best Triptan for Migraine: Abort Attacks with the Right Medication

3. Ergotamine Medications
Older acute migraine medicines: dihydroergotamine (injection, nasal spray), ergotamine tartrate (tablets, suppositories).
Effective for some people, especially when triptans fail, but carry more severe side effect risks; not for long-term frequent use.
Ergot Alkaloids relieve migraine or cluster headache symptoms by stimulating the chemical serotonin which is needed to transmit various nerve signals to the brain.
It decreases inflammation and reverses blood vessel dilation surrounding the brain.
Here are just a few to add to the list of migraine medications:
- Dihydroergotamine (DHE-45) is available by self-injection and as a nasal spray called Migranal®.
- Methysergide (Sansert) - rarely used due to side effects
- Ergotamine Tartrate (Bellamine, Cafergot®, Ergostat) - with caffeine
Ergotamine preparations are normally made up by a compounding chemist making them more expensive and potentially hard to get. Ergotamine is the oldest "first line" of treatment. It is also known to have more severe side effects than some of the more recent medications.
Watch out for stomach or chest pain, tingling in your fingers and toes, blurred vision or any weakness experienced in your limbs. Please note - these drugs must not be taken for prolonged periods over weeks or months due to these high risks.
My body quickly rejected Cafergot on a number of occasions. The suppository made me vomit almost instantly for hours. So much for that! This was not a good medication for me. I wish you better luck with this one. My doctor takes this for her migraine attacks because of its track record of successes.
Warning: Higher risk of vascular side effects - never use long term.
4. Newer Migraine Medications: CGRP Inhibitors & Gepants
The latest treatments target calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) - a protein involved in migraine attacks.
- Examples: Aimovig® (erenumab), Ajovy® (fremanezumab), Emgality® (galcanezumab), Nurtec ODT® (rimegepant), Ubrelvy® (ubrogepant)
- How they work: Block CGRP or its receptor to prevent or stop migraines
- Best for: People who haven’t responded to triptans or have frequent attacks
Note: CGRP drugs can be costly, but insurance coverage is improving. They’re often considered when standard preventives fail.
Newer Acute Medications
Gepants: ubrogepant, rimegepant (oral) - CGRP receptor antagonists, well-tolerated, minimal heart risks.
Ditans: lasmiditan - works via serotonin 5HT1F pathway; may cause dizziness and impair driving.
** Please Note **
[1] The medications on this page can have similar or very different names in every different country. [2] ALL medications on this list of migraine medications have side effects. Please treat them with caution.
5. Preventive Migraine Medications
For use with frequent attacks or poor acute control.
The goal of preventative treatment medications is to decrease the regularity and severity of your migraine attacks.
First line preventives (treatment medications your doctor should try first):
- Beta-blockers: Propranolol (Inderal®, Timolol®), Timolol (Blocadren®), metoprolol
- Anticonvulsants: Topiramate (Topamax®), Valproate or Divalproex sodium (Depakote®)
- CGRP monoclonal antibodies: erenumab, fremanezumab, galcanezumab, eptinezumab
- Botulinum toxin A (Botox®) - for chronic migraine
It is essential that you take the adequate dose of the medicine for a sufficient length of time in order to determine its effectiveness for your migraine. If you are experiencing side effects, talk with your doctor to titrate or reduce your dose.
6. Additional Preventive Options
If none of the four preventatives above work for you, don't give up hope. Here is a list of prevention alternatives:
Antidepressants: Amitriptyline (Endep®, Elavil®), Nortriptyline ( Aventyl®, Pamelor®)
Anti-seizure medications: Gabapentin (Neurontin®), Sodium Valproate (Epilim®)
Beta-blockers: Nadolol (Corgard®), Metoprolol (Lopressor®)
Calcium channel blockers: Verapamil (Covera®), Diltiazem ( Dilacor®)
Minerals: magnesium supplementation for deficiency; lithium carbonate (specialist use)
7. Anti-Nausea Medications
Used with acute treatments to improve absorption and comfort:
- Metoclopramide (Reglan®)
- Prochlorperazine (Compazine®)
- Promethazine (Phenergan®)
8. Minerals for Migraine Prevention
Minerals to Calm Nerve and Muscle Cells:
- Magnesium - often low in migraine patients
- Lithium carbonate - for certain migraine patterns
Magnesium - It is common for migraine sufferers to have low magnesium blood levels. It took me over two years to get my level up with regular intravenous magnesium pushes. If you experience confusion, jerking muscle movements, muscle weakness, or an uneven heart rate tell your doctor asap. You could be low in this vital mineral that calms the muscles and nerves.
Lithium Carbonate - Lithium affects the flow of sodium through nerve and muscle cells in the body to reduce the intensity of excitation and mania.
My favorite magnesium supplement for stress, sleep, and migraine prevention.
Some drugs are used in the treatment for headaches but are not specific for migraines.
These include analgesics, narcotics, and barbiturates. Since they can be addictive, they are less desirable than the list of migraine medications provided above.
Choosing the Best Option
1. Once you have your migraine diagnosis - discuss goals - i.e. rapid relief vs fewer attacks.
2. Jot down a few medications from this list that sound right for you or buy the printable list!
3. Take the whole list or your top 3 (shortlist) to your doctor and discuss ALL your options.
4. Trial one medication at a time.
5. Track results in a diary. Keeping good records is essential.
6. Work with your doctor to adjust dose or switch as needed.
My advice: Start with one class (often triptans for acute) before moving to others. If one triptan doesn't work try another one. They all work a little differently. Consider preventives if you get breakthrough pain and if attacks are frequent.
Get Your Printable Migraine Medication List
Easily compare options, mark your preferences, and take to your doctor.
Price: $4.99 - Instant Download via PayPal
>> Get Your Copy Now <<
List of Migraine Medications FAQs
1. What is the most effective migraine medication?
1. What is the most effective migraine medication?
Answer: That depends on the patient, but triptan injections (sumatriptan) often work fastest; gepants are an option for those with heart concerns.
2. Can I buy migraine medications online?
2. Can I buy migraine medications online?
Answer: Use only licensed pharmacies; counterfeit risk is high online.
3. What’s new in migraine treatment?
3. What’s new in migraine treatment?
Answer: Gepants and CGRP monoclonal antibodies are newer, targeted options for acute and preventive care.
4. What is the difference between triptans and gepants?
4. What is the difference between triptans and gepants?
Answer: Triptans are serotonin (5-HT1B/1D) agonists used for acute attacks but are contraindicated in some heart conditions. Gepants are oral CGRP receptor antagonists used for acute treatment (and some for prevention) and generally don’t carry the same cardiovascular restrictions. Discuss options with your clinician.
Get Your Printable Migraine Medication List Here
Instant download - $4.99 via PayPal
<< Go back to Migraine Medications
MIGRAINE MEDICATIONS Related Articles
List of Migraine Medications References:
1. The National Headache Foundation (NHF 2016) Headache Fact Sheets: Migraine.
2. The USFDA (2016) Patient Information Medication Guide: Treximet™ at: www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm089804.pdf.
3. Evidence Based Migraine Treatments (2017) Available [Online]: https://migrainepal.com/evidence-based-acute-migraine-treatments/
4. American Academy of Neurology migraine guidelines
5. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2015) Acute migraine treatment efficacy
6. FDA medication approvals list 2025